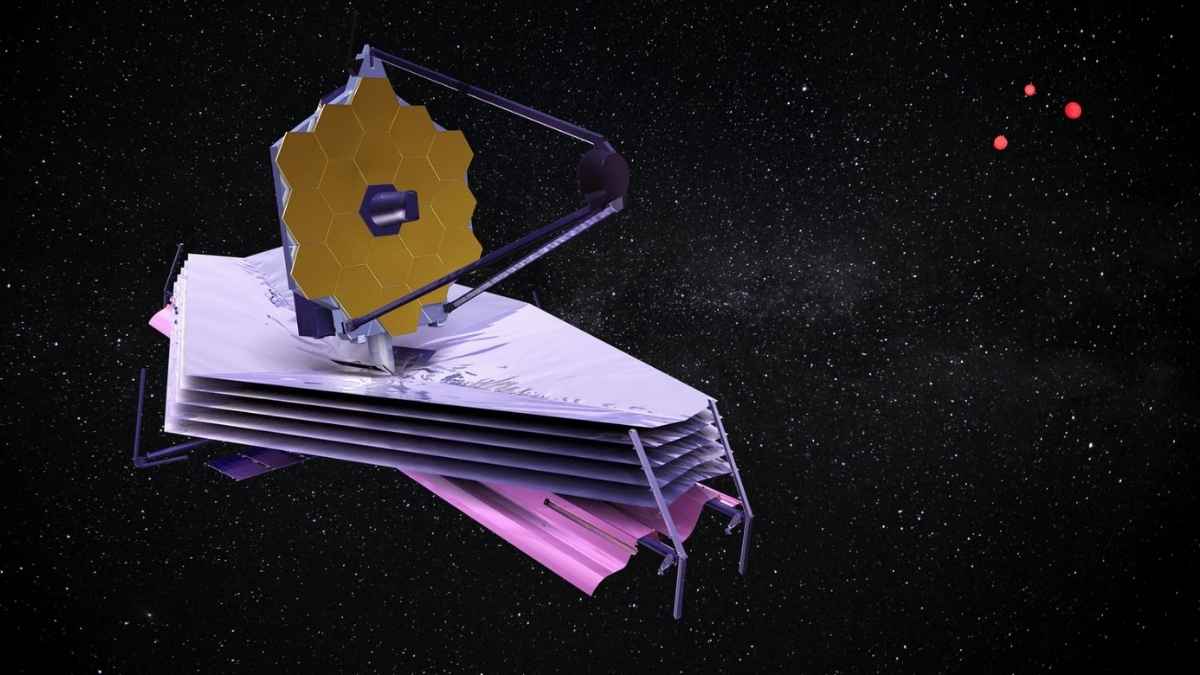
The universe once again shows us its most enigmatic side. NASA astronomers have identified three small red dots in data obtained by the James Webb Space Telescope. Despite decades of exploration, the agency has not found a convincing explanation for the phenomenon, which points to previously unexplored corners of the cosmos. The scientific community is beginning to wonder if these three red dots could be the initial clue to an even bigger process. The official announcement was made during the 245th meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Maryland in January 2025, and has generated intense debate about the nature of these objects.
The scientific context: the relevance of the James Webb telescope in studies of the early cosmos
The James Webb telescope, launched into space in December 2021, has become the main window into the beginnings of the universe. Thanks to its ability to scrutinize infrared wavelengths, it reveals details that previous instruments, such as the veteran Hubble, could not capture.
These red dots form part of a set of findings that could include compact galaxies, with only 0.1% visible matter and 99% of their composition still unknown. The reddish color suggests extreme redshift, which would indicate that these are objects remote in time and space.
Official research: NASA describes hundreds of black holes and possible clues as to their origin
Parallel to the appearance of these enigmatic red dots, NASA confirmed the existence of hundreds of black holes roaming unexplored regions of the universe. Some astronomers believe that, in some way, both phenomena could be connected, implying processes of early formation of cosmic structures.
During the American Astronomical Society conference, preliminary results were also presented that point to the possibility that today’s giant galaxies originated from much more compact concentrations. Scientists hope to correlate these supposed nuclei with the three detected red dots, to better understand the role of supermassive black holes.
The experts’ analysis: how the small red dots could change current galactic theories
Specialists such as astrophysicist Dale Kocevski, from Colby College, emphasize that the small red dots existed when the universe was barely a billion years old. Subsequently, their trail seems to have vanished. They could be primitive galaxies whose light was stretched by cosmic expansion, or the active centers of enormous structures in formation.
Cosmological models, therefore, face uncertainty: if these objects are stars or mature galaxies at such a high redshift, current theory could require significant adjustments. However, if we are talking about black holes or transitory phenomena, the view of the evolution of the universe would be maintained, albeit with notable nuances.
Additional context: comparison with previous phenomena and links with other recent space research
For months now, new mysteries have been reported on planets such as Uranus and Neptune, as well as multiple indications of unknown activity in distant corners of space. The James Webb telescope, a million miles from Earth and with a budget of approximately 10 billion dollars, never ceases to amaze with images capable of defying the human imagination.
In this sense, the enigmatic red dots join a growing list of discoveries that include unusual galactic formations and huge black holes roaming uninhabited regions of the cosmos.
Each of these findings highlights the fact that our knowledge is still limited. Stay tuned and informed thanks to the section where you will see more news related to science and that you can find from this own digital newspaper.